The Intel's 8253 and 8254 are programmable interval timers designed to interface with MCU microcontrollers to implement counting and timing and other simple functions.
How the 8253 and 8254 works
One of the big problems solved by these integrated circuits (8253/8254) is the very precise timing functionality compared to those managed in software in microcontrollers.
Each of these circuits contains three 16-bit counting registers. Each register has:
- Two input pins: CLK input and GATE input
- An output pin: OUT
To start the counting operation, one starts to reload register by a value and on a command register, it starts decrementing the value of that register (countdown timer) until it is equal to zero.
Once the zero value in this register is reached, the circuit generates interrupts on channel (IRQ) which can subsequently be used either by a microcontroller or another electronic stage. the circuit generates a pulse which can subsequently be used either by a microcontroller or another electronic stage.
What’s the difference between 8253 and 8254
The 8254 Timer:
- Three PIT channels:
- Three Independent 16-Bit Timer Tick Counters
- Binary or BCD Counting
- Status Read-Back Command
- Six Programmable Timer Modes.
- Handles Inputs from DC to 10 MHz (with independent frequency dividers)s from DC to 10 MHz (with independent frequency dividers)om DC to 10 MHz
- 8 MHz 8254
- 10 MHz 8254-2
The 8253 Timer:
- Three PIT channels:
- Handles Inputs from DC to 2,6 MHz (with independent frequency dividers)
- Three Independent 16-Bit Timer Tick Counters
- No Binary or BCD Counting
- No Status Read-Back Command
- Six Programmable Timer Modes
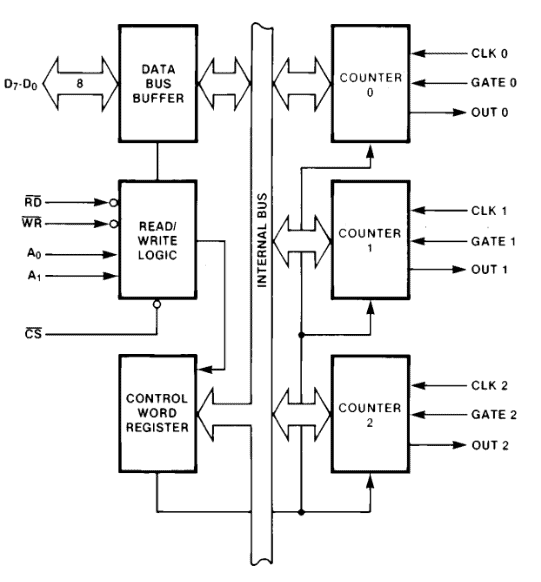
Block Architecture of 8253 or 8254
Here after we can find the block representation of the hardware architecture of the 8253/8254 chips:
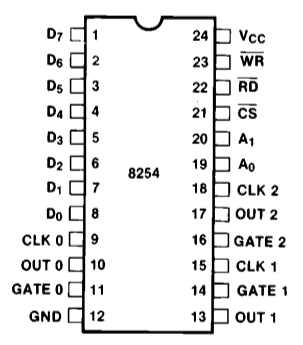
Pin Configuration of 8253 or 8254
Here after we can find the pinout of the 8253/8254 chips:
Operating Modes of 8253 or 8254
The 8253/8254 PIT Timer chip offers a variety of operational modes tailored for precise timing, event counting, and signal generation in microprocessor systems.
- Mode 0 – Interrupt On Terminal Count
- Mode 1 – Hardware Re-triggerable One-shot
- Mode 2 – Rate Generator
- Mode 3 – Square Wave Generator
- Mode 4 – Software Triggered Strobe
- Mode 5 – Hardware Triggered Strobe
Features of 8253 or 8254
Other main functions that can be implemented with these circuits:
- Programmable Rate Generator
- Periodic Timers
- Event Counter
- Binary Rate Multiplier
- Real Time Clock
- Digital One-Shot
- Complex Motor Controller
Main Asked Questions about 8253 and 8254
- What is a programmable interval timer in operating system?
- What is the difference between 8253 and 8254 programmable interval timers?
- How to create an interval timer?
- What is the Intel 8254 programmable interval timer?
- What does an interval timer do?
- Is 8254 a microprocessor or microcontroller?
- How does the 8253 timer work?
- What is a programmable timer?
- What is the function of the interval timer chip?
- What are the modes of 8254 timer?
- How is 8254 used as a square wave generator?
- What is 8254 clock gating?
- What is the basic difference between 8253 and 8254 timers?
- What is the function to stop an interval timer?
- What is the default interval for system timers timer?
- How does an interval timer work?
- Which is called an interval timer?
- What is an interval timer relay?
- What is programmable delay timer?
- How do timers work in programming?
- What is PLC timer and counter?
- What is the difference between a timer and a counter?
Conclusion
The 8253 or 8254 remain an essential component of timing and system control, providing accuracy, flexibility and reliability in applications that require precise timing and counting.





